Kubernetes has revolutionized container orchestration, enabling organizations to deploy and manage applications at scale. Autoscaling is a fundamental feature of Kubernetes that dynamically adjusts resources based on workload demands.
While CPU and memory-based horizontal scaling serve as common metrics, they often fail to capture the full complexity of modern applications. This blog post will explore how Kubernetes Event-driven Autoscaling (KEDA) can address these challenges effectively.
Kubernetes Event-driven Autoscaling (KEDA)
Kubernetes Event-driven Autoscaling (KEDA) is an open-source component for Kubernetes that enhances autoscaling capabilities by enabling event-driven scaling based on custom metrics and external triggers. It extends the standard Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) in Kubernetes, allowing for more flexible and granular autoscaling.
Here are some of the features of KEDA
- Event-driven autoscaling: KEDA can scale applications based on external events, such as the number of messages in a Kafka topic or the number of events in an Azure Event Hub. This allows you to scale your applications in real time to meet demand.
- Built-in scalers: KEDA comes with a built-in catalogue of scalers for various cloud platforms, databases, messaging systems, telemetry systems, CI/CD, and more. This makes it easy to get started with event-driven autoscaling.
- Support for multiple workload types: KEDA supports a variety of workload types, such as Deployments, Jobs, and custom resources with the /scale subresource. This makes it a flexible solution for a wide range of applications.
- Extensible: KEDA is extensible, so you can bring your own scalers or use community-maintained scalers. This gives you the flexibility to meet the specific needs of your applications.
- Cost Savings: KEDA can help you save money on cloud costs by scaling your applications to zero when they are not needed. This can be a significant savings, especially for applications that have variable workloads.
- Vendor-agnostic: KEDA is vendor-agnostic, so you can use it with any Kubernetes cluster. This makes it a great choice for organizations that want to use Kubernetes on-premises, in the cloud, or at the edge.
- Simplified Configuration and Management: KEDA provides a declarative approach to configuration through Kubernetes manifests. You can define autoscaling rules and triggers using YAML or JSON files, making it easy to configure and manage autoscaling behaviour for your applications.
Let’s See KEDA In Action
Let’s explore how KEDA can be used in GKE to perform autoscaling based on pub/sub message metrics. The sample application and kubernetes manifest files are available in the GitHub repo.
Prerequisites
- A GKE cluster with workload identity enabled
- Helm and Kubectl
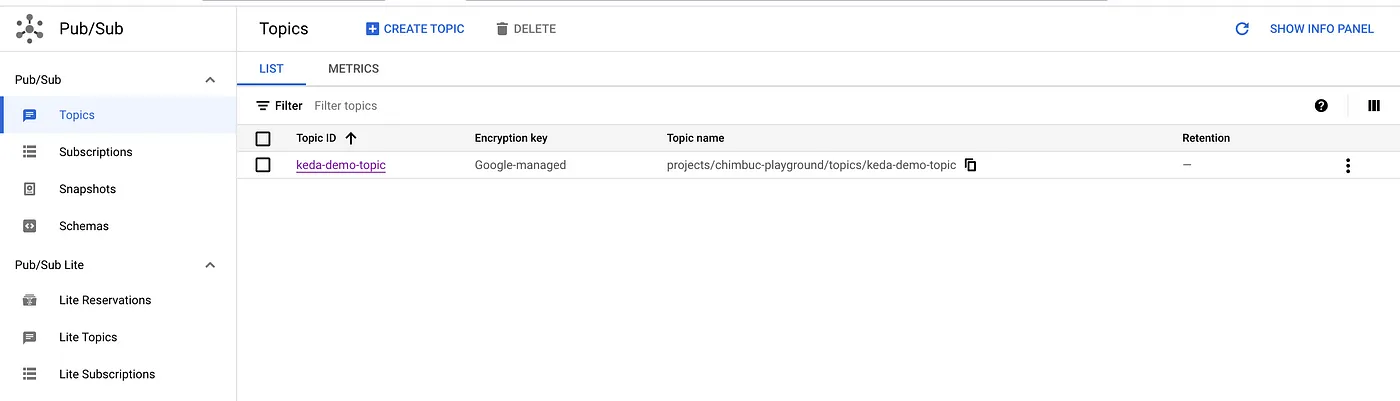
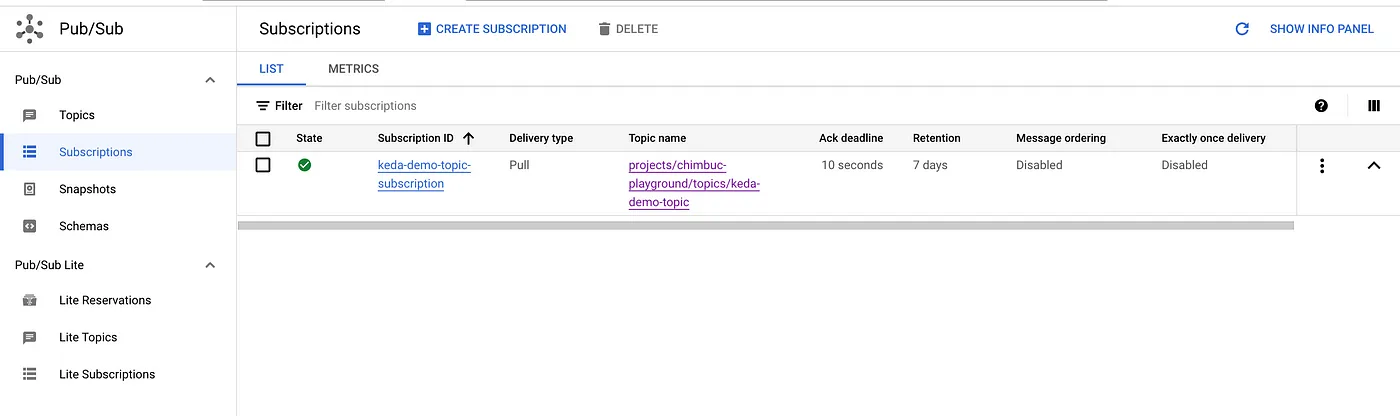
Setup Pub/Sub resources
Run the below commands to set up a pub/sub topic and subscription.
GCP_PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value project) TOPIC_NAME=keda-demo-topic SUBSCRIPTION_NAME=keda-demo-topic-subscription # Create Topic gcloud pubsub topics create $TOPIC_NAME --project $GCP_PROJECT_ID # Create Subscription gcloud pubsub subscriptions create $SUBSCRIPTION_NAME \ --topic $TOPIC_NAME \ --project $GCP_PROJECT_ID
Setup Workload Identity for KEDA
GCP Workload Identity allows workloads in GKE clusters to impersonate Identity and Access Management (IAM) service accounts to access Google Cloud services. Workload Identity is the recommended way for workloads running on GKE to access Google Cloud services in a secure and manageable way.
Run the below commands to set up workload identity for KEDA.
KEDA_GCP_SERVICE_ACCOUNT=keda-operator
KEDA_NAMESPACE=keda
KEDA_K8S_SERVICE_ACCOUNT=keda-operator
#Create GCP service account
gcloud iam service-accounts create $KEDA_GCP_SERVICE_ACCOUNT \
--project=$GCP_PROJECT_ID
#Create IAM role bindings
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $GCP_PROJECT_ID \
--member "serviceAccount:$KEDA_GCP_SERVICE_ACCOUNT@$GCP_PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role "roles/monitoring.viewer"
#Allow kubernetes service account to impersonate GCP service account
gcloud iam service-accounts add-iam-policy-binding $KEDA_GCP_SERVICE_ACCOUNT@$GCP_PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com \
--role roles/iam.workloadIdentityUser \
--member "serviceAccount:$GCP_PROJECT_ID.svc.id.goog[$KEDA_NAMESPACE/$KEDA_K8S_SERVICE_ACCOUNT]"
Install KEDA
Below are the various options which can be used to install KEDA on Kubernetes Cluster.
We will use Helm Chart to deploy KEDA in the GKE cluster.
- Add and update the Helm repo.
helm repo add kedacore https://kedacore.github.io/charts helm repo update
- Install the latest KEDA helm chart.
helm upgrade -install keda kedacore/keda \ --namespace keda \ --set 'serviceAccount.annotations.iam\.gke\.io\/gcp-service-account'="$KEDA_SERVICE_ACCOUNT@$GCP_PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \ --create-namespace \ --debug \ --wait
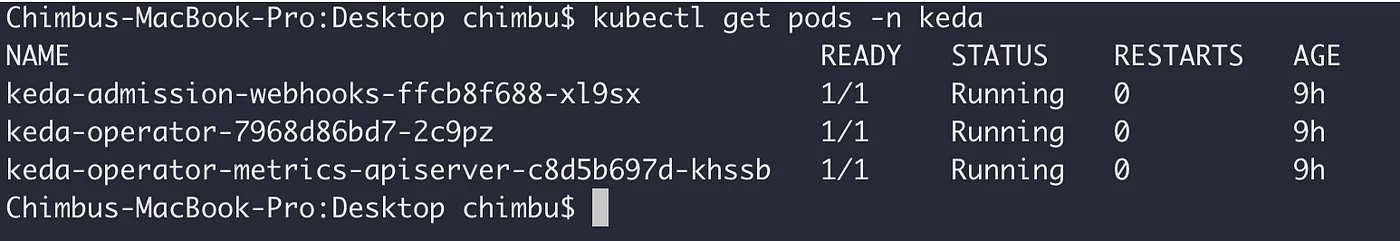
Verify the kedapods logs and ensure the application is running without any errors.
The KEDA webhook calls are served over port 9443, So ensure any firewall rule between the control plan -> node allows the request over port 9443. In GKE, the auto-generated firewall rules only allow communication over ports 443,10250, and you need to create a new firewall to allow the over port 9443.
Sample gcloud firewall rule command.
gcloud compute firewall-rules create allow-api-server-to-keda-webhook \ --description="Allow kubernetes api server to keda webhook call on worker nodes TCP port 9443" \ --direction=INGRESS \ --priority=1000 \ --network=$VPC-NETWORK-NAME \ --action=ALLOW \ --rules=tcp:9443 \ --source-ranges=$CONTROL-PLANE-IP-RANGE \ --target-tags=$NETWORK-TAGS-ASSIGNED-TO-NODES
Deploy the sample application
Set up workload identity for the sample application to consume the messages from the pub/sub subscription.
SAMPLE_APP_GCP_SERVICE_ACCOUNT=keda-demo
SAMPLE_APP_NAMESPACE=default
SAMPLE_APP_K8S_SERVICE_ACCOUNT=keda-demo
#Create GCP service account
gcloud iam service-accounts create $SAMPLE_APP_GCP_SERVICE_ACCOUNT \
--project=$GCP_PROJECT_ID
#Create IAM role bindings
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding $GCP_PROJECT_ID \
--member "serviceAccount:$SAMPLE_APP_GCP_SERVICE_ACCOUNT@$GCP_PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role "roles/pubsub.subscriber"
#Allow kubernetes service account to impersonate GCP service account
gcloud iam service-accounts add-iam-policy-binding $SAMPLE_APP_GCP_SERVICE_ACCOUNT@$GCP_PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com \
--role roles/iam.workloadIdentityUser \
--member "serviceAccount:$GCP_PROJECT_ID.svc.id.goog[$KEDA_NAMESPACE/$KEDA_SERVICE_ACCOUNT]"
Deploy the sample application to the GKE cluster.
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
annotations:
iam.gke.io/gcp-service-account: keda-demo@$GCP_PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com
name: keda-demo
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: keda-demo
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: keda-demo
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: keda-demo
spec:
serviceAccountName: keda-demo
containers:
- image: simbu1290/keda-demo:v1
name: consumer
env:
- name: PUB_SUB_PROJECT
value: $GCP_PROJECT_ID
- name: PUB_SUB_TOPIC
value: "keda-demo-topic"
- name: PUB_SUB_SUBSCRIPTION
value: "keda-demo-topic-subscription"
EOF
Deploy KEDA Event Scaler
KEDA seamlessly integrates with various Scalers (event sources) and utilizes Custom Resources (CRDs) to specify the necessary/desired scaling actions and parameters. KEDA monitors the event source and feeds that data to Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) to drive the rapid scale of a resource.
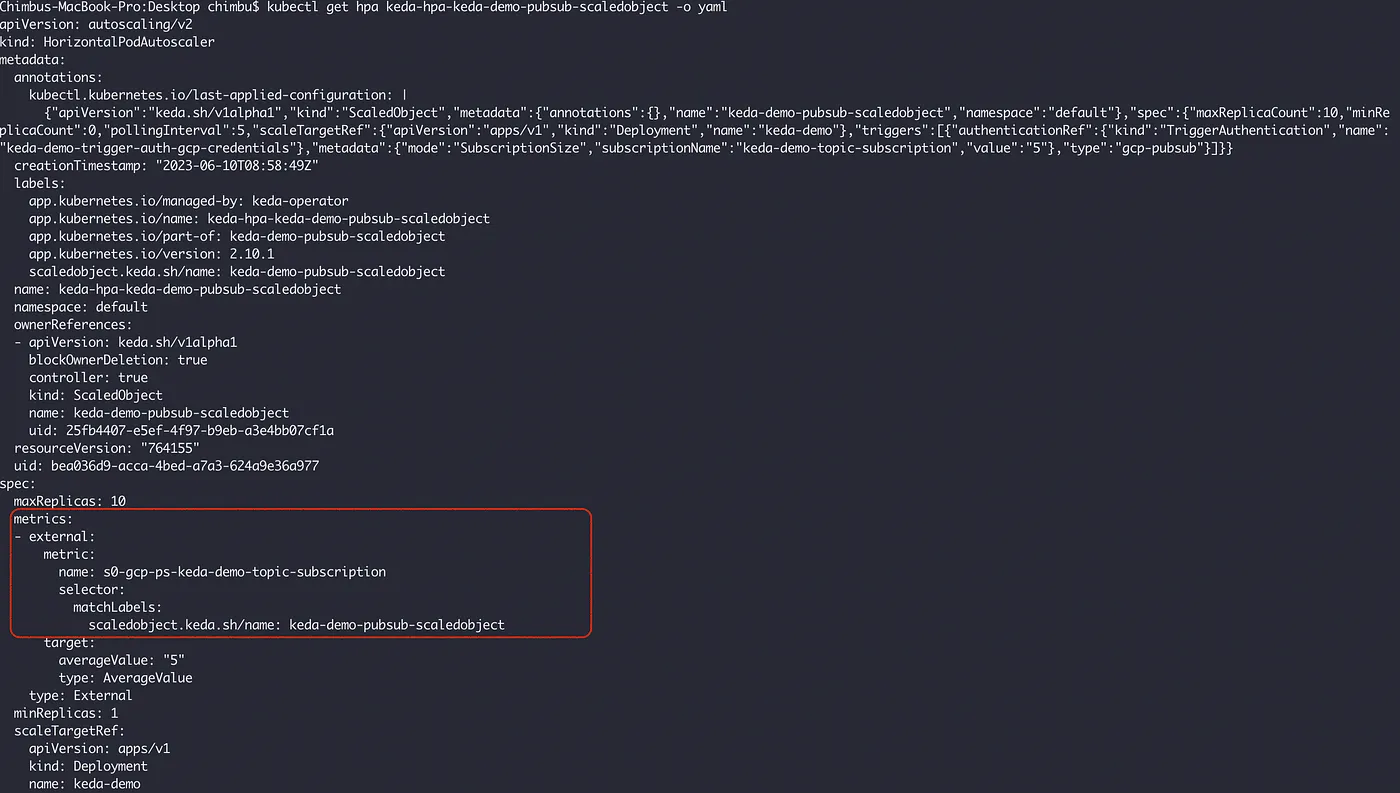
Here we will use Google Cloud Platform Pub/Sub event scaler to demonstrate Auto Scaling. The scaling relationship between an event source and a specific workload (i.e., Deployment, StatefulSet) is configured using the ScaledObject Custom Resource Definition.
TriggerAuthentication allows you to describe authentication parameters separate from the ScaledObject and the deployment containers. It also enables more advanced authentication methods like pod identity and authentication re-use.
Deploy the below resources for autoscaling, and KEDA will perform scaling based on the number of unacknowledged messages in the subscription.
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
---
apiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1
kind: TriggerAuthentication
metadata:
name: keda-demo-trigger-auth-gcp-credentials
spec:
podIdentity:
provider: gcp
---
apiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1
kind: ScaledObject
metadata:
name: keda-demo-pubsub-scaledobject
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1 # Optional. Default: apps/v1
kind: Deployment # Optional. Default: Deployment
name: keda-demo # Mandatory. Must be in the same namespace as the ScaledObject
pollingInterval: 5 # Optional. Default: 30 seconds
minReplicaCount: 1 # Optional. Default: 0
maxReplicaCount: 10 # Optional. Default: 100
triggers:
- type: gcp-pubsub
authenticationRef:
kind: TriggerAuthentication
name: keda-demo-trigger-auth-gcp-credentials
metadata:
mode: "SubscriptionSize" # Optional - Default is SubscriptionSize - SubscriptionSize or OldestUnackedMessageAge
value: "5" # Optional - Default is 5 for SubscriptionSize | Default is 10 for OldestUnackedMessageAge
subscriptionName: "keda-demo-topic-subscription" # Mandatory
EOF
Explore the HPA resource created by KEDA.
Use the below script to publish test messages to the topic and observe the scaling actions performed by HPA based on the metrics provided by KEDA.
#!/bin/bash
project_id=$GCP_PROJECT_ID
topic_name=$TOPIC_NAME
while true; do
message="Hello, Pub/Sub!"
gcloud pubsub topics publish ${topic_name} \
--message "${message}" \
--project ${project_id}
sleep 1
done
KEDA scaling demo
Conclusion
In this blog, we explored the functionality of KEDA by demonstrating its usage in an application that scaled based on GCP Pub/Sub metrics.
KEDA has proven to be a valuable tool for event-based scaling in Kubernetes environments, allowing organizations to efficiently scale their applications while customizing metrics and responding to real time events. By leveraging KEDA, organizations can optimize costs and resource management, ensuring their applications are dynamically scalable and responsive to workload demands.