Kubernetes has transformed container orchestration, and Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) provides a powerful, managed platform for deploying and scaling containerised applications. While GKE offers strong capabilities for service discovery and load balancing, there are still limitations on applying custom processing logic to traffic before it reaches the workloads.
This is where Service Extensions come into play, providing a compelling solution to customise and enhance the Cloud Load Balancing with the GKE Gateway API (Note: This is a kubernetes feature and unrelated to Google Cloud API Gateway Service).
What are Service Extensions in GCP?
Service Extensions enables users to inject custom logic directly into the data path, enabling advanced modifications to traffic that flows through the load balancer. It's like a pipeline where you can insert your own code at various stages to manipulate the requests and responses without impacting the backends.
There are two primary types of Service Extensions:
- Plugins: These allow for inline custom code insertion directly within the networking data path. Built using WebAssembly (Wasm) and the Proxy-Wasm ABI, plugins run as Wasm modules on a Google-managed sandbox infrastructure. They are designed for low-latency operations and are ideal for light-weight logic that needs to execute very close to the data plane.
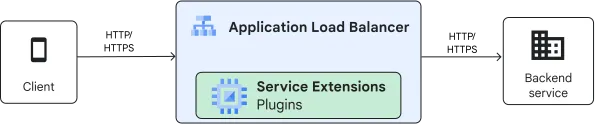
- Callouts: These enable Cloud Load Balancing to make gRPC calls to external services — either Google-managed services or user-managed services (including those running on GKE Pods). Callouts offer greater flexibility as they can reuse existing software and have fewer runtime restrictions, making them suitable for more complex logic that might require external data or state.
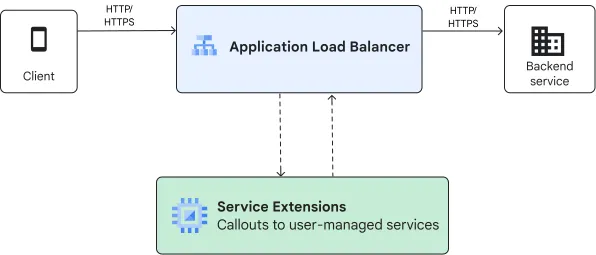
The GKE team recently announced preview support for Service Extensions in the Gateway API. This allows users to manipulate HTTP headers and payloads for requests and responses and even control traffic routing, all without impacting the existing backend service selections or security policies.
Types of GKE Gateway API Service Extensions
GKE Gateway controller currently supports two types of Callouts Service Extensions, each designed for specific functionalities:
GCPRoutingExtension: This extension type is focused on controlling traffic routing. It's ideal for scenarios where you need to direct traffic to different backend services or apply custom routing logic.
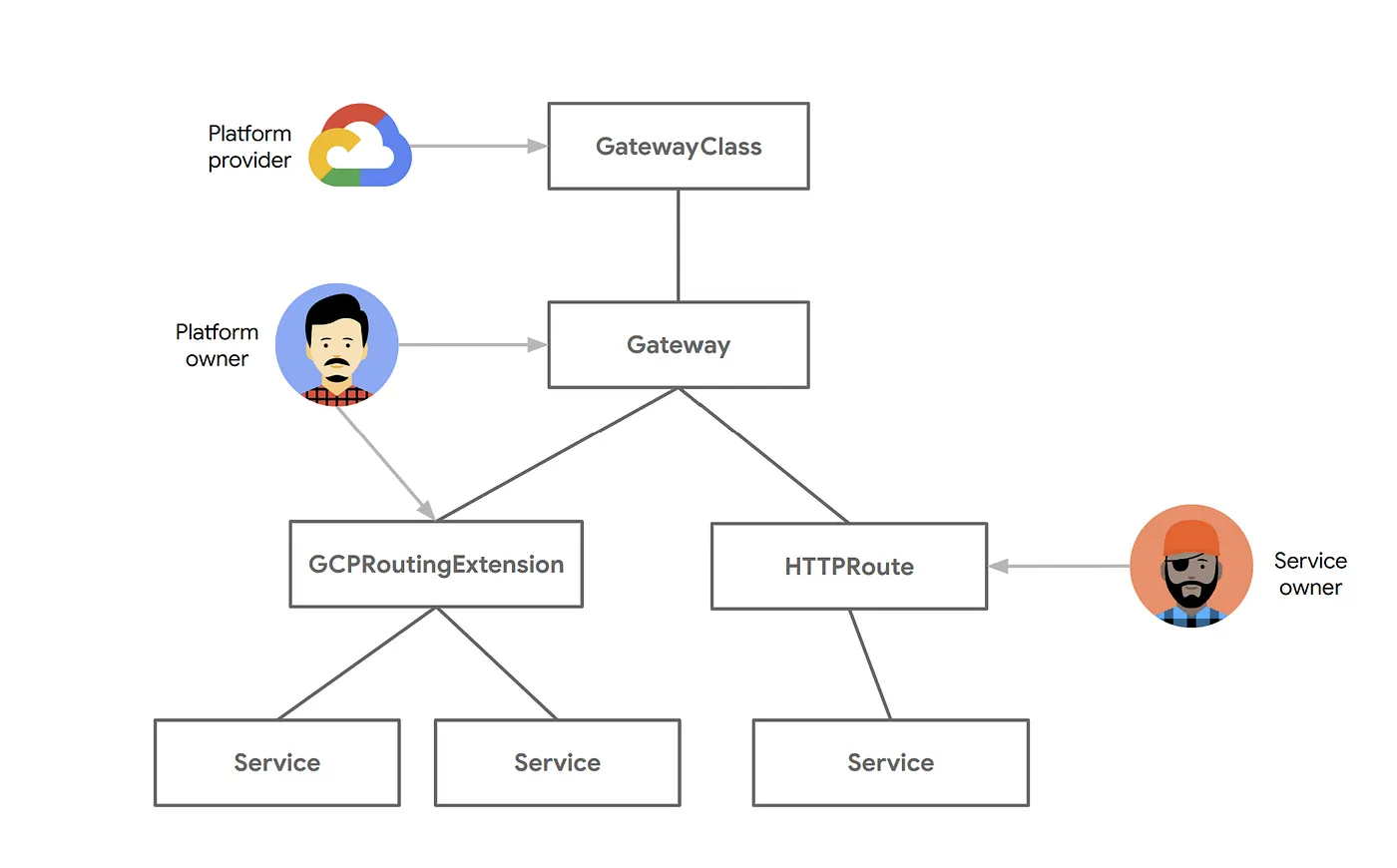
GCPTrafficExtension: This extension type allows you to change the headers and payloads of requests and responses. It operates without affecting backend service selection or security policies, making it perfect for data transformation and enrichment.
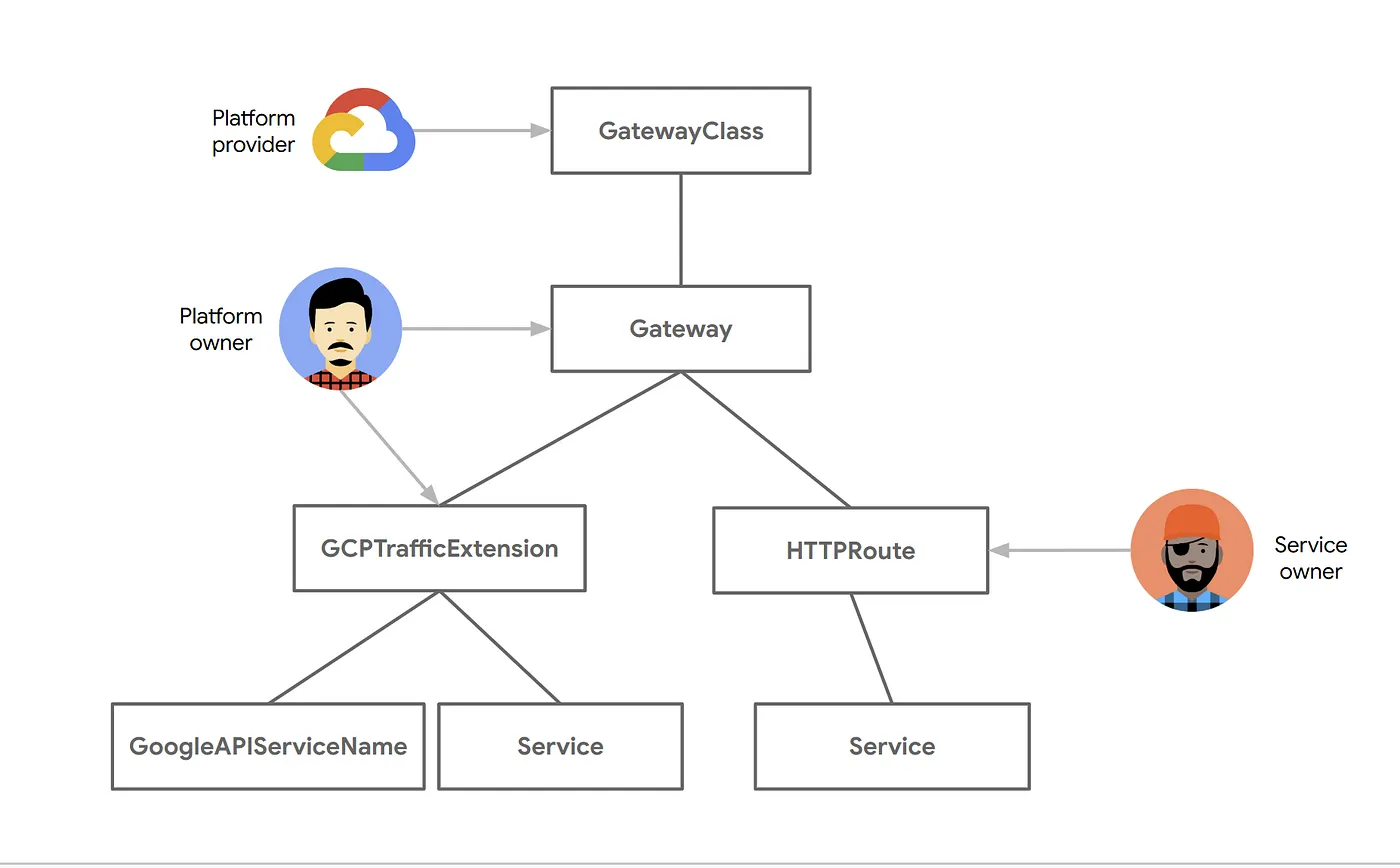
Configure Service Extensions in GKE Gateway API
To explore the service extension feature in GKE, you need a GKE cluster with version 1.33 or later and Gateway API enabled. Also, review the current Restrictions and limitations of Gateway Service Extensions in GKE before testing this feature.
Deploy a Gateway
To configure a Service extension, you must first deploy a Gateway resource or verify that the existing Gateway resource uses a supported GatewayClass. For details on supported load balancers, refer to Google Cloud Service Extension compatibility with GatewayClasses.
- Apply the below manifest to deploy a simple regional application load balancer gateway.
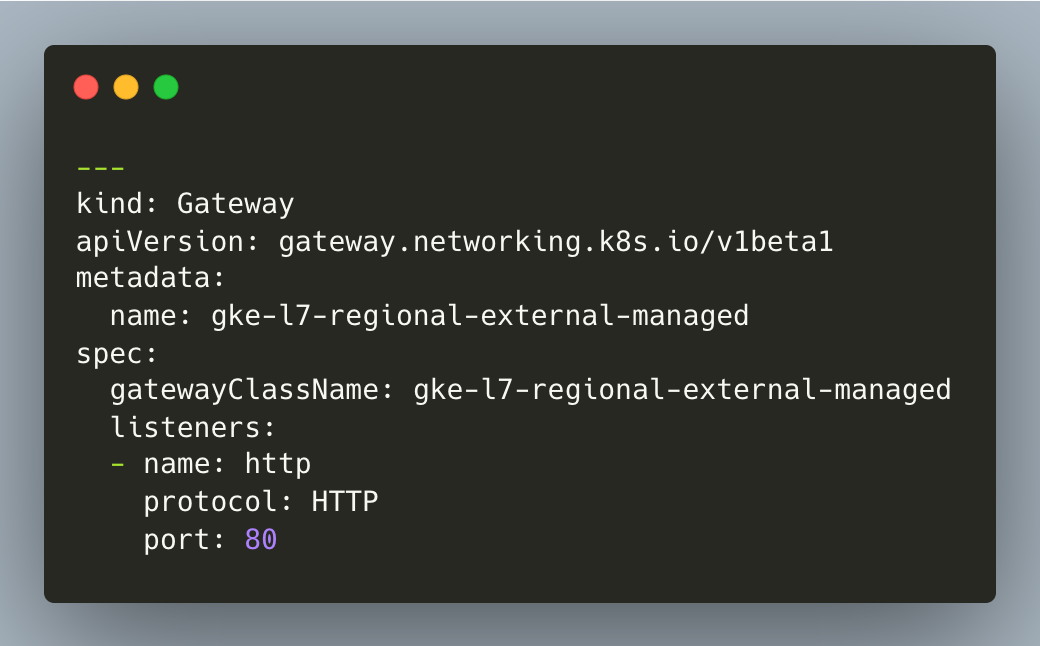
Deploy a sample store backend application
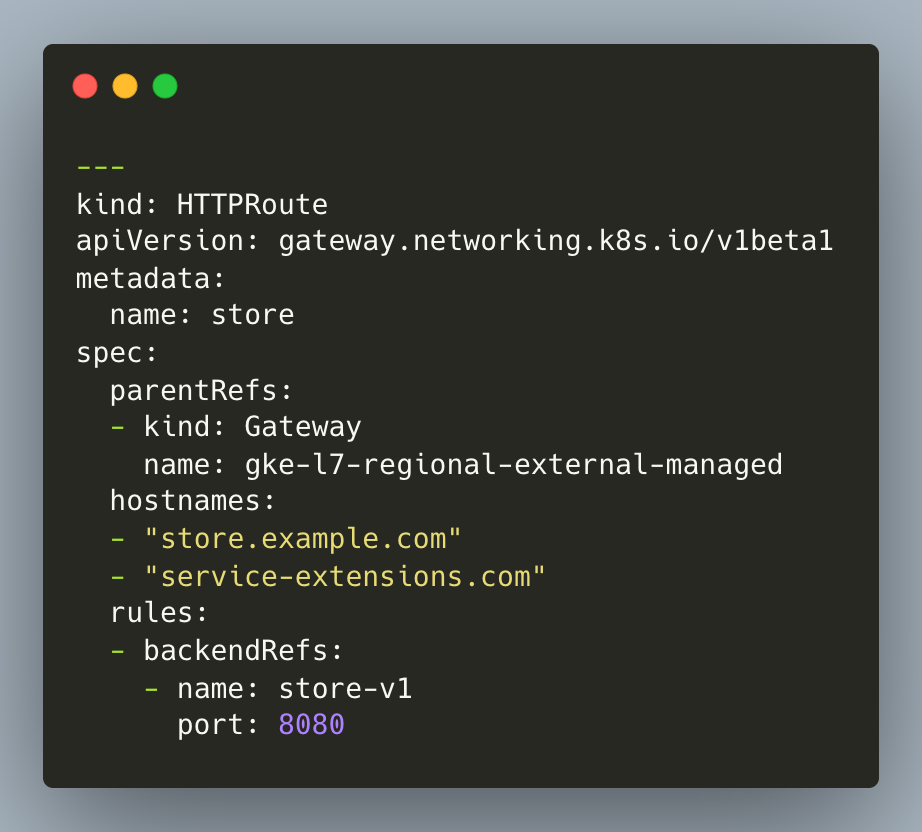
- Apply the below manifest to deploy the sample backend application and HTTPRoute resources. The HTTPRoute specifies the routing behaviour of HTTP requests from a Gateway listener to the backend application.
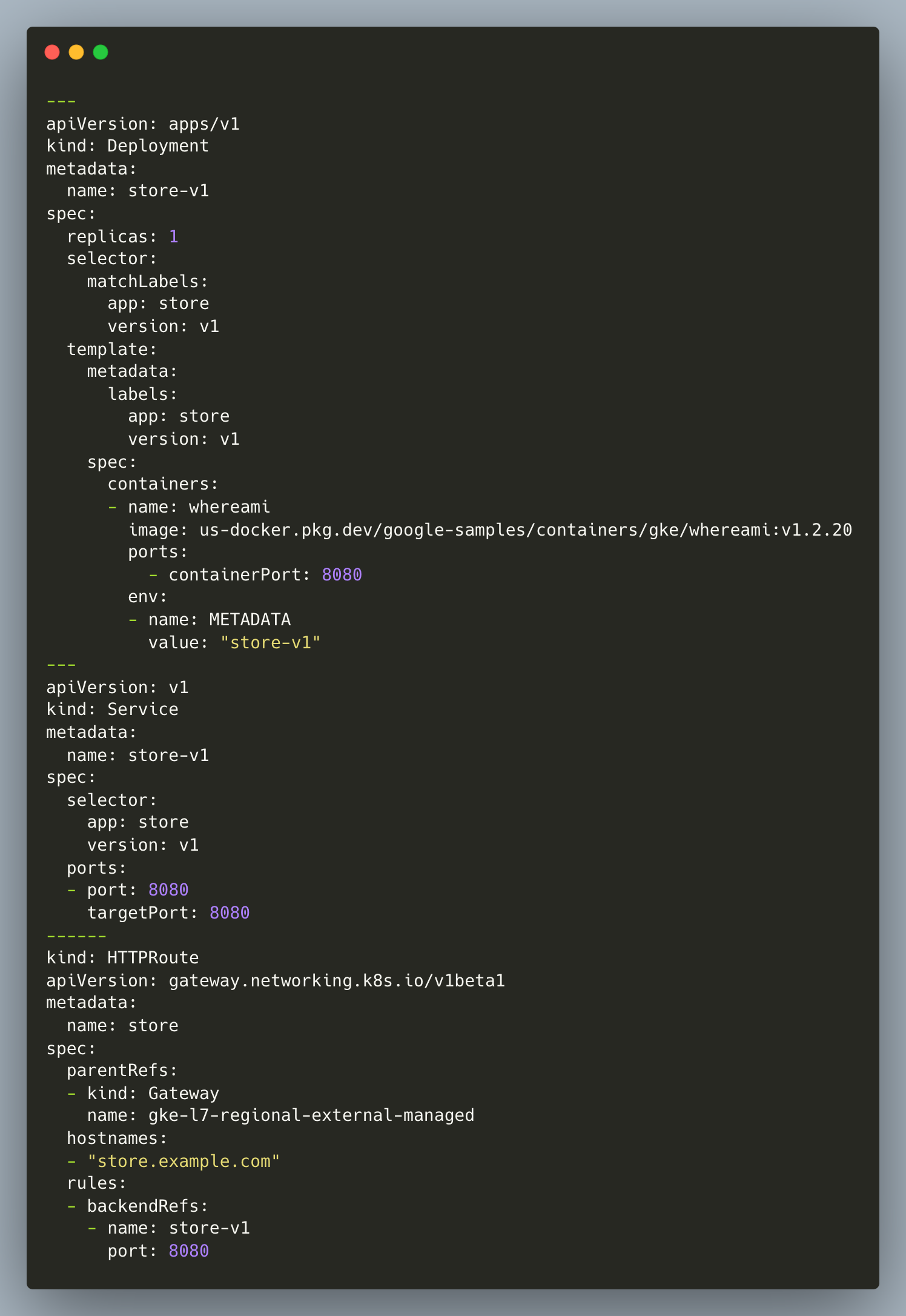
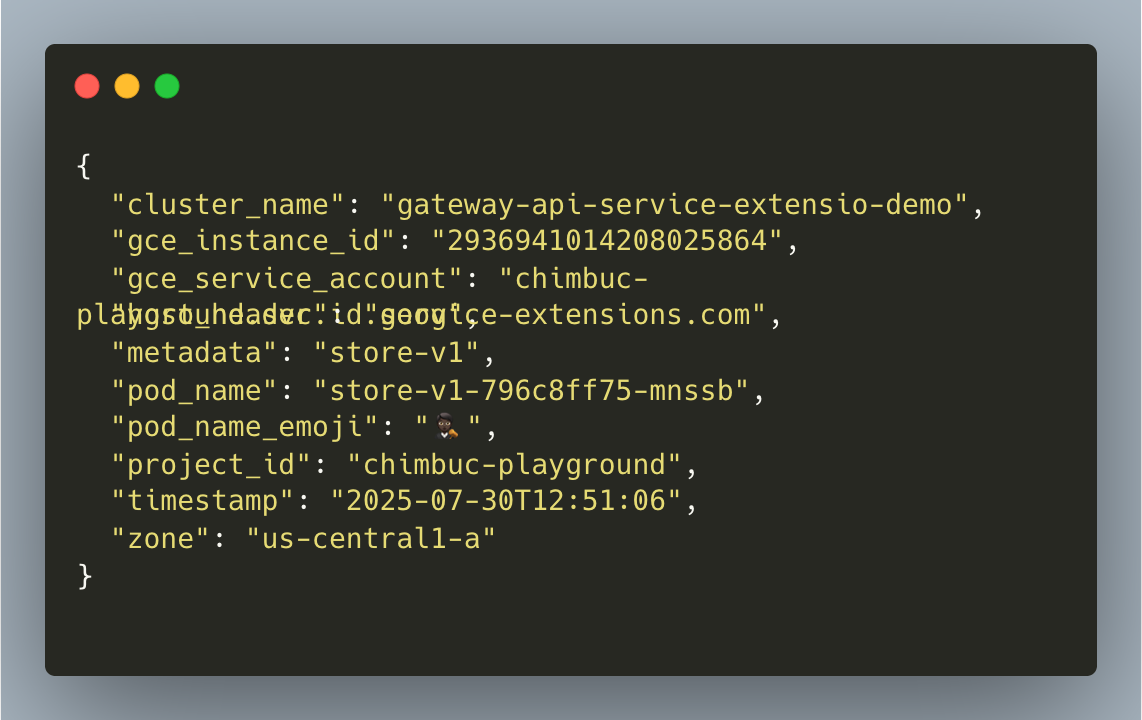
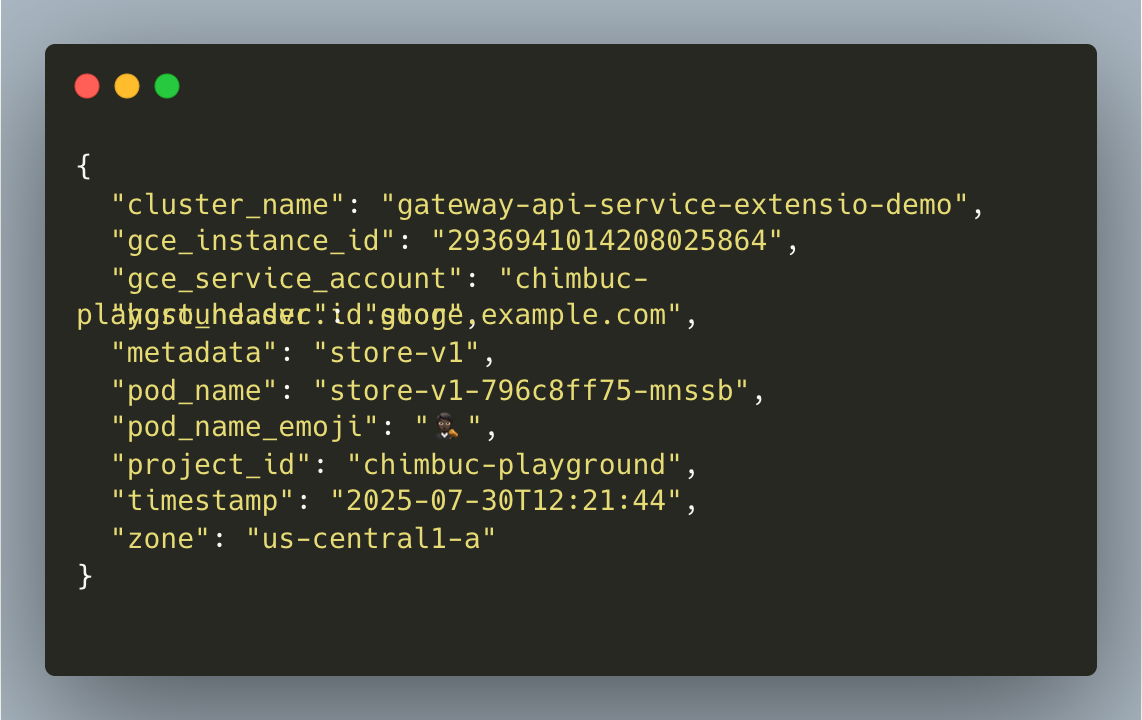
- Send a sample request to the gateway API IP address to test the backend response.
The output is similar to the following:
Deploy a backend callout service
A callout service implements the custom logic for Gateway Service Extensions in GKE. The Load Balancer invokes the backend applications based on GCPTrafficExtension or GCPRoutingExtension configurations, to modify or route traffic.
If you are deploying a callout service in the GKE cluster, you must meet all the requirements mentioned in the limitations.
- Generate a self-signed certificate for the callout service backend using mkcert or any other method. This is necessary because you must use HTTP2 as it's
appProtocolwhich requires end-to-end TLS.
- Create a K8S Secret with the self-signed cert.
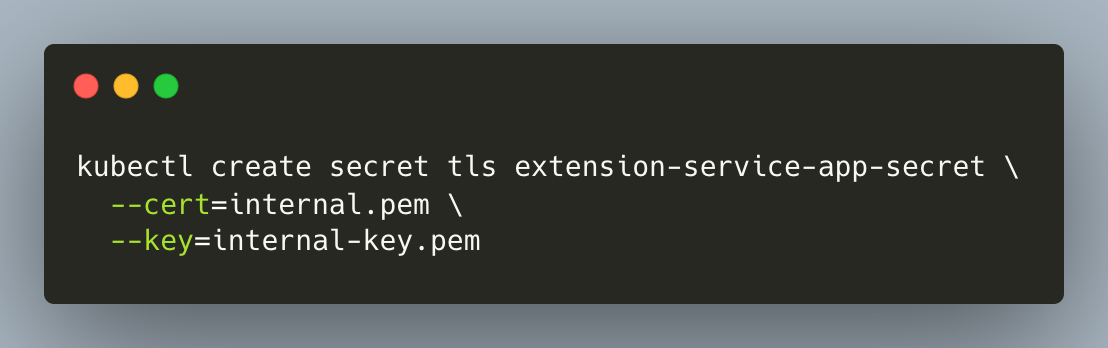
- Apply the manifest below to deploy the sample callout application. For more code samples, refer to the service-extensions GitHub repository.
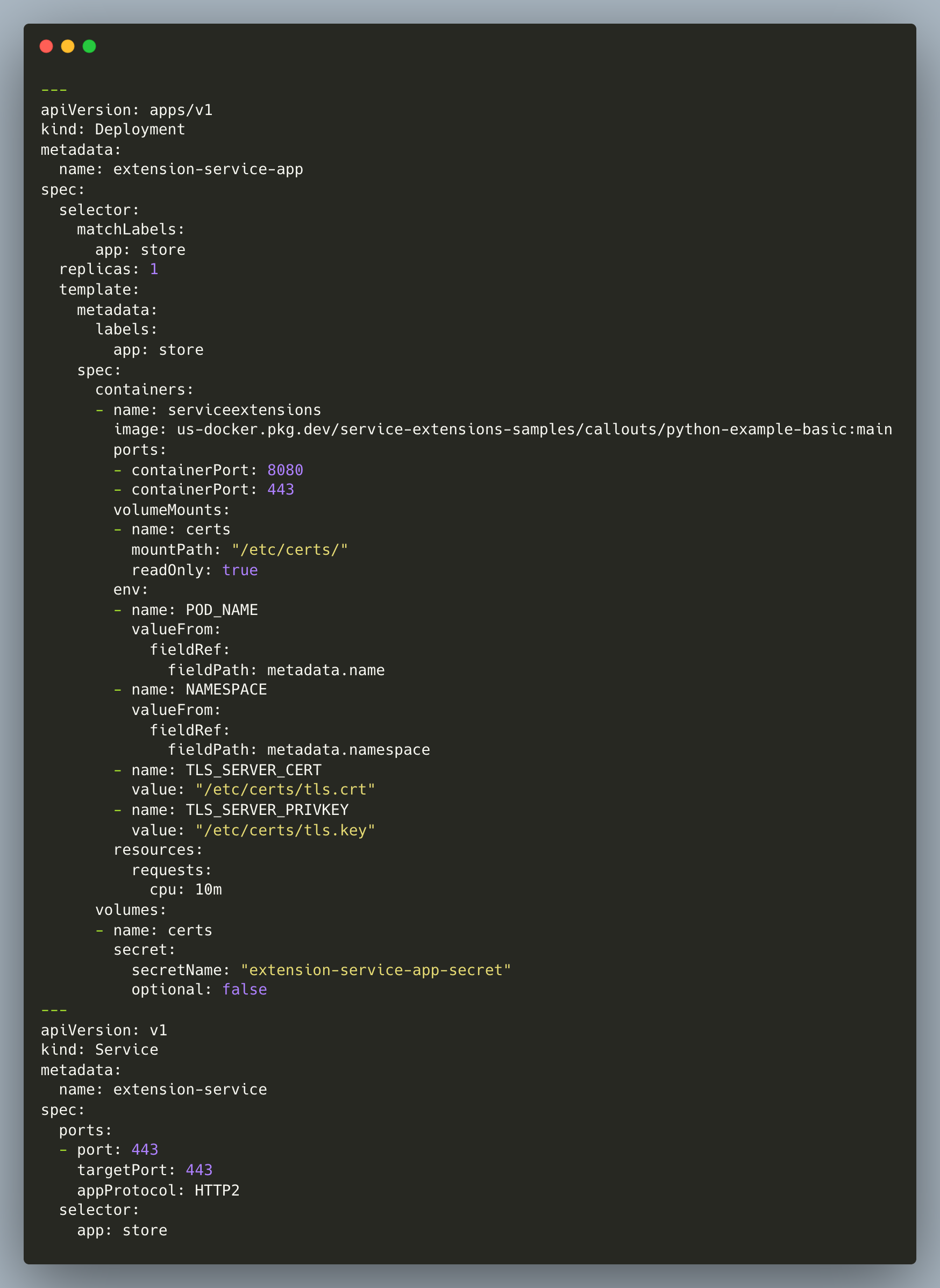
- The sample application performs a basic header modification for both the request and response. Refer to service_callout_example.py for further details, and you can develop your own application based on the business requirements.
Configure the Service Extensions
You can configure either a GCPRoutingExtension or a GCPTrafficExtension to customize your traffic flow.
- Apply the manifest below to create a
GCPRoutingExtensionresource, and the load balancer will call the extension service app for the requests sent to the pathrouteextensionand then forward it to the backend store application.

- Update the
HTTPRouteresource withservice-extensions.comhost since the callout service performs a host header modification before forwarding the requests to the store app.
- The Gateway API controller may take a few minutes to sync the changes. Use the command
kubectl describe gateway GATEWAY_NAMEto confirm that theGCPRoutingExtensionis bound to the Gateway.
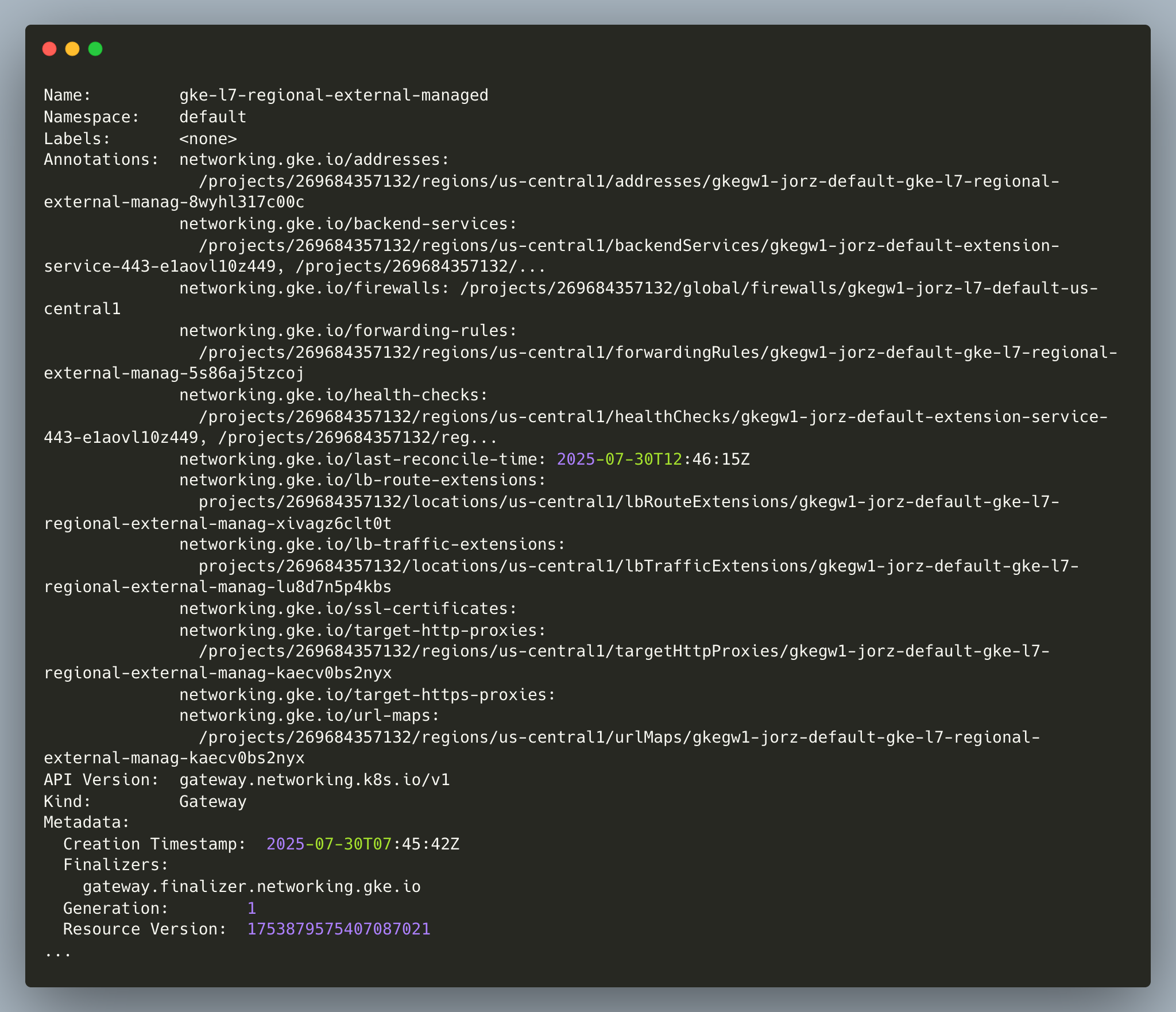
- The output shows the annotations, which GKE uses to store the links between the Gateway and the underlying Google Cloud resources. The
networking.gke.io/lb-route-extensionsannotation confirms the binding of the gateway to theGCPRoutingExtension. - Now test the traffic to the
routeextensionpath by replacingGATEWAY_IP_ADDRESS.

- The output resembles the following, and you can notice the changes in the
host_headerwithin the response.
You can use GCPTrafficExtension to implement custom request and response logic, sophisticated routing, transformations, and security policies.
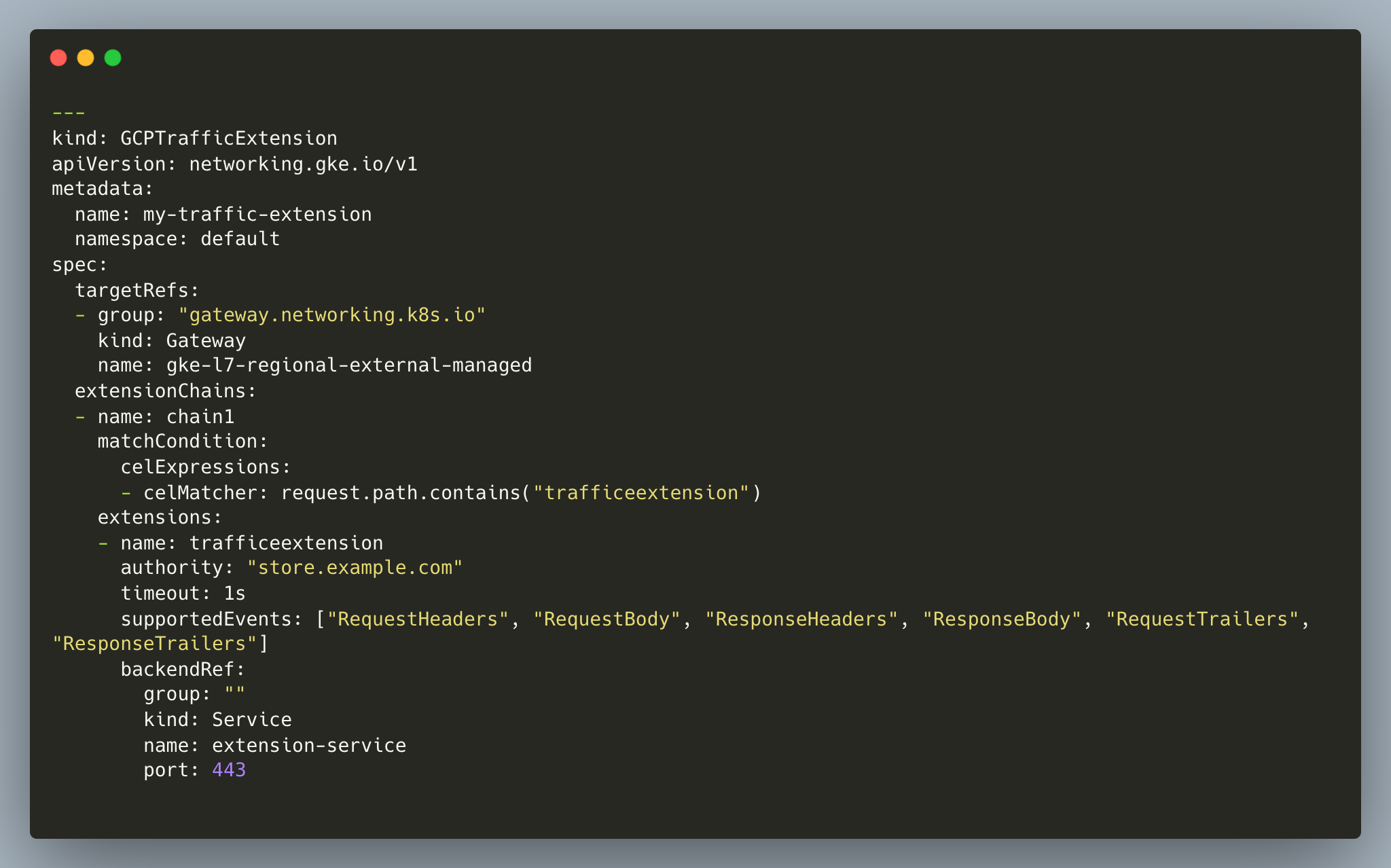
- Apply the manifest below to create a
GCPTrafficExtensionresource, and the load balancer will call the extension service app for the requests sent to the pathtrafficetension. You can customize and control the load balancer invocation to the callout application by updating thesupportedEvents.
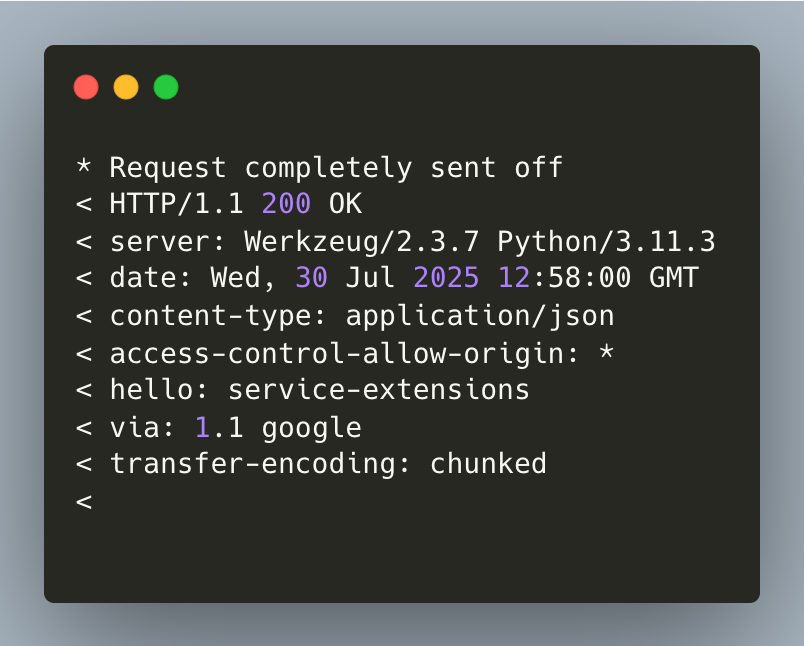
- Now test the traffic to the
trafficextensionpath by replacingGATEWAT_IP_ADDRESS.

- The output resembles the following, and you can notice the customer response header changes in
helloand the response body is removed.
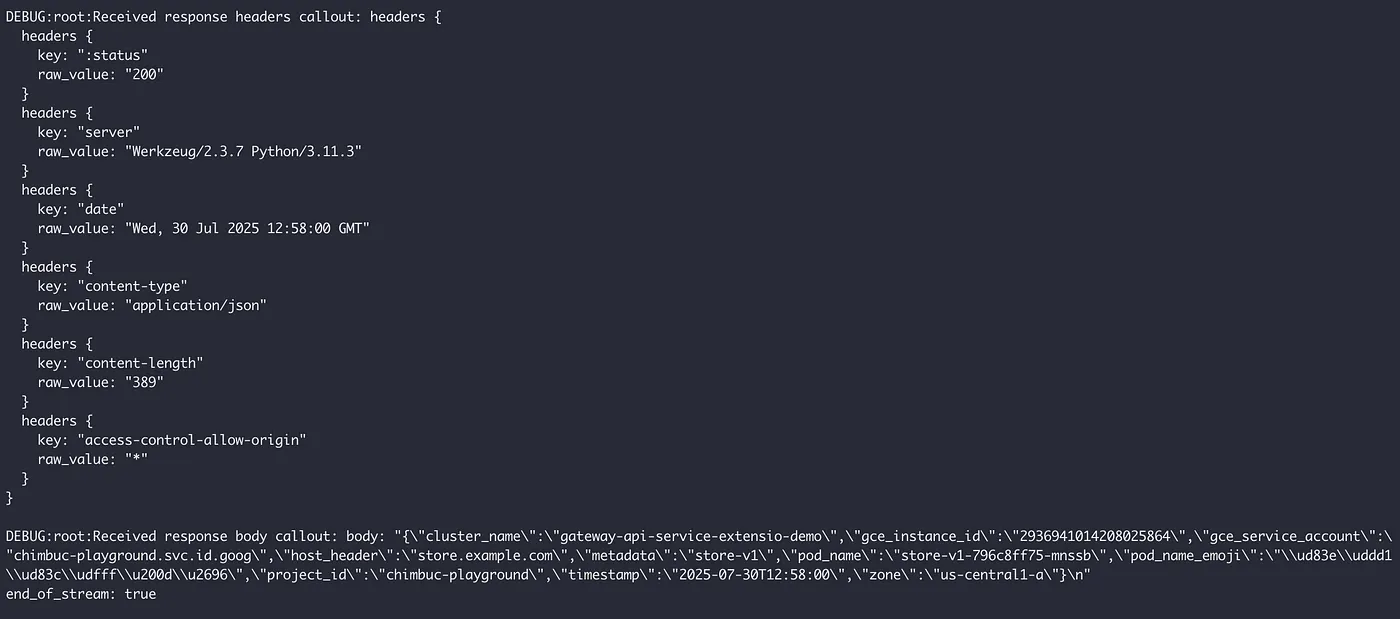
Sample Pod logs:
Conclusion
GCP Service Extensions for GKE Gateway API represent a significant advance in how platform teams can manage, shape, and secure traffic at the ingress layer. Whether you need to enforce custom authentication, manipulate headers, perform traffic shaping, or integrate with external systems, Service Extensions enable you to do so declaratively and scalably.
Although it is still in preview, this presents an excellent opportunity to explore Service Extensions, test them in non-production environments, and develop reusable extension services tailored to your platform requirements.
If you are considering a PoC, you are not alone. DoiT is here to help you assess, plan and migrate with a strong focus on your business outcomes. With over 100 senior cloud experts specializing in crafting customized cloud solutions, our team is ready to help you navigate this process smoothly and optimize your infrastructure to ensure compliance and meet future demands efficiently.
Our experts are ready to provide you with strategic guidance and technical expertise every step of the way. Let’s discuss what makes the most sense for your company during this policy enforcement phase, ensuring your cloud infrastructure is robust, compliant, and optimized for success. Contact us today.