Kubernetes has become a key technology in cloud computing, and it can revolutionize how your organization deploys, scales, and manages containerized applications. As an open-source container orchestration system, it simplifies managing distributed systems, letting applications run reliably across different environments. How can Kubernetes work for your company? By automating deployment, scaling, and recovery, Kubernetes can help your organization streamline operations and focus on innovation.
If your organization is seeking efficiency and reliability, Kubernetes offers tools to help you achieve these goals. These tools enable teams to manage systems with confidence and improve workflows. With features like load balancing, automated rollouts, and scaling, Kubernetes is all but essential for DevOps. It can optimize resources while keeping your applications resilient.
What is Kubernetes architecture?
Before we get into Kubernetes architecture, it’s important to understand containerization and its impact on application deployment. Containerization is like a lightweight version of virtualization. It bundles an application along with all its dependencies (like libraries, binaries, and config files) into one portable package called a container. Unlike traditional virtual machines that need a full operating system for each instance, containers share the host system’s OS kernel, making them more efficient and quicker to start up.
Containerization is a lightweight alternative to traditional virtualization, sharing the host OS kernel to reduce overhead, start faster, and use fewer resources. Containers provide consistent environments and enable “build once, run anywhere” functionality.
Kubernetes simplifies managing large-scale container deployments with features like scalability, automation, self-healing, and a strong ecosystem, making it a leading container orchestration platform. It provides a reliable framework for handling the complexities of distributed computing environments with efficiency and precision. For example, in a traditional environment, your team would have to manually manage the deployment and scaling of applications. This process is time-consuming, error-prone, and difficult to maintain as the infrastructure grows.
By automating tasks with a single API, Kubernetes makes things easier, letting you manage containers across different environments. It also comes with self-healing features, so it can recover from failures on its own without any help. With Kubernetes, your team can smoothly roll out new app versions while keeping everything running and responsive, even during heavy traffic.
Let’s lay out the basics of how Kubernetes tackles some of the biggest challenges in software deployment:
- Automatic scaling: Kubernetes adjusts resources in real time based on application demand, ensuring your system can handle fluctuations without manual intervention.
- Self-healing capabilities: If a container fails, Kubernetes detects the issue and automatically replaces it, keeping your applications running smoothly.
- Zero-downtime updates: With seamless rollouts and rollbacks, updates can be implemented without disrupting users, minimizing downtime.
- Advanced networking: Kubernetes manages complex networking needs, providing smooth communication between multiple containers in distributed systems.
- Intelligent resource utilization: Workload scheduling is optimized to make the best use of infrastructure, helping you control costs while maintaining performance.
Kubernetes simplifies the challenges of managing containerized applications, allowing you to concentrate on building and running software without the burden of managing infrastructure. Here are some key benefits of using Kubernetes:
- Flexibility: Deploy applications with ease across a variety of environments.
- Consistency: Maintain reliable performance, whether on-premises, with cloud providers, or in hybrid environments.
- Efficiency: Reduce operational overhead by automating routine management tasks.
- Scalability: Effectively manage complex, distributed systems without added difficulty.
- Cost optimization: Improve resource utilization to manage costs more effectively. For teams that want to continuously optimize resource requests and node efficiency, PerfectScale for Kubernetes by DoiT provides automated analysis and actionable recommendations based on real workload behavior.
When you're ready to implement Kubernetes, you have excellent managed service options from major cloud providers. Amazon's Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), and Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) take care of the heavy lifting for you. These services handle the complex tasks of managing your control plane, automating updates, and maintaining high availability.
Each comes with its own strengths—EKS integrates seamlessly with AWS services, GKE offers advanced autoscaling features, and AKS provides strong Azure DevOps integration. By choosing a managed service, you can focus on your applications while the provider handles the infrastructure complexities.
Ultimately, since it offers practical solutions to make your workflow easier and can fit your specific needs, Kubernetes simplifies the challenges of managing applications.
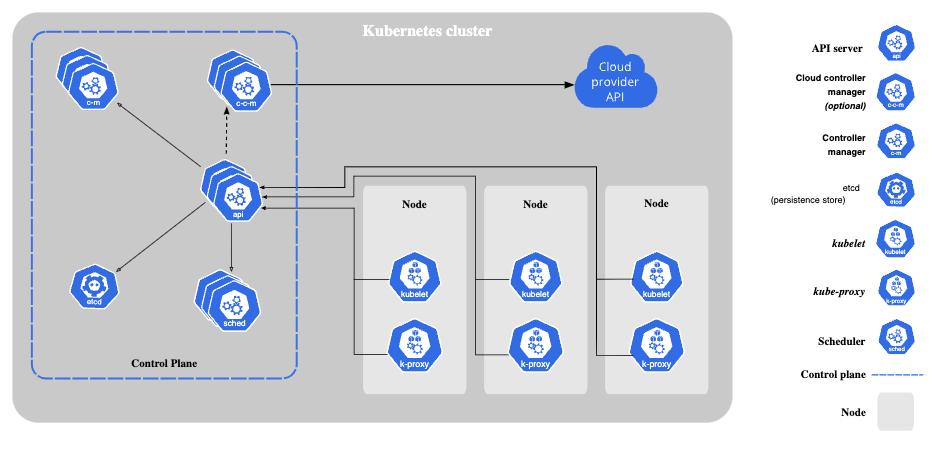
The core Kubernetes architecture components
(Source)
Kubernetes architecture is built around two core components: the control plane and the worker nodes. This structure is designed to provide a reliable, scalable, and flexible platform for managing containerized applications. By separating responsibilities between these components, Kubernetes allows for efficient orchestration and can simplify scaling and managing workloads.
Kubernetes control plane architecture
The control plane oversees a Kubernetes cluster—a group of worker machines (called nodes) that run containerized applications. In Kubernetes, the cluster is the backbone of your deployment, bringing together all the machines and resources needed to run your apps as one cohesive, manageable unit.
Control plane components include:
kube-apiserver
kube-apiserver is the central management component of a Kubernetes cluster. It works by:
- Providing access to the Kubernetes API, which serves as the main entry point for interacting with the cluster.
- Managing administrative tasks and overseeing cluster state to keep everything running smoothly.
- Acting as the primary interface for cluster interactions, allowing you to control and manage operations effectively.
etcd
etcd is a distributed and consistent key-value store that plays a critical role in Kubernetes architecture. Its key benefits include:
- Serving as the primary data storage mechanism for the cluster, maintaining the complete state of the system.
- Keeping your cluster’s data secure and recoverable with reliable configuration backups.
- Providing stability and reliability with consistent state management across the entire cluster.
- Minimizing downtime through high availability enabled by its distributed architecture.
kube-scheduler
The kube-scheduler is responsible for determining the best placement for pods within a Kubernetes cluster. When scheduling pods, the kube-scheduler takes several factors into account:
- Resource requirements: Ensures the pod has the CPU, memory, and other resources it needs.
- Hardware/software constraints: Matches the pod to nodes that meet specific hardware or software needs.
- Affinity and anti-affinity rules: Respects rules that define which pods should be placed together (or kept apart).
- Data locality: Places pods closer to the data they need to minimize latency.
- Performance optimization: Balances workloads across nodes to enhance cluster performance.
kube-controller-manager
The kube-controller-manager oversees multiple controller processes to maintain the cluster’s desired state. Key controllers include:
- Node controller: Monitors node health and status to ensure nodes are working properly.
- Replication controller: Maintains the correct number of pod replicas running as specified.
- Endpoints controller: Manages the population of service endpoints for efficient communication.
- Service account & token controllers: Handles authentication and manages access tokens for secure operations.
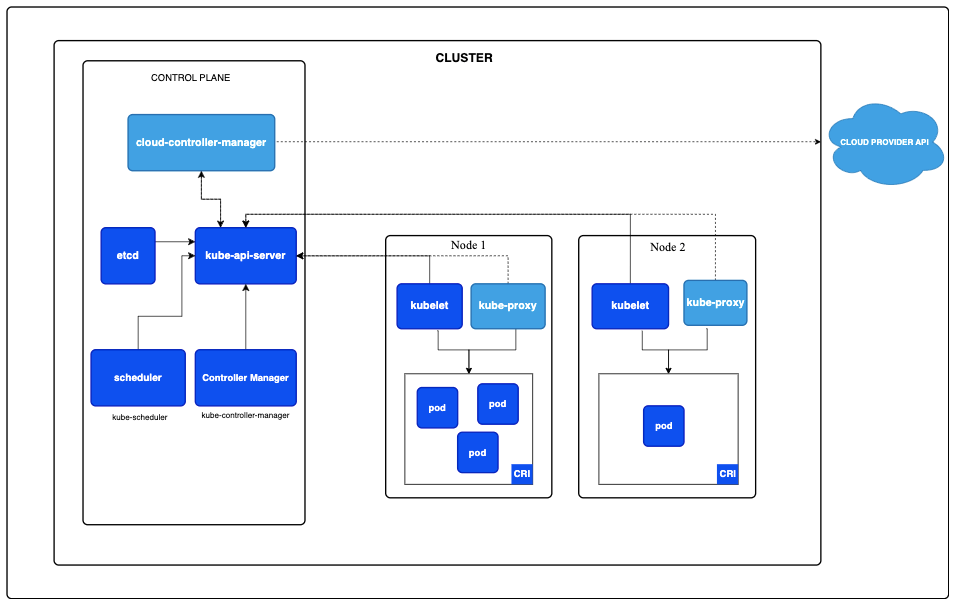
Kubernetes node architecture
(Source)
Worker nodes are the computational engines of the Kubernetes cluster, running your containerized applications. These nodes are essentially the computing resources you’re paying for in your cloud setup, so the number and size of them will directly affect your costs. When it comes to cutting Kubernetes expenses, organizations often focus on making better use of their nodes. Tweaking node counts, improving bin-packing, and selecting the right node sizes can make a big difference.
To improve efficiency and reduce waste across clusters and workloads, PerfectScale for Kubernetes by DoiT helps teams continuously rightsize requests and limits, improve pod placement, and identify idle resources. For additional product details, you can also visit PerfectScale.
Worker nodes include the following components:
kubelet
The kubelet is the primary node agent in Kubernetes. It’s responsible for several key tasks that ensure the smooth operation of your cluster:
- Communicating with the control plane: The kubelet regularly checks in with the control plane to receive instructions and report the node's status and workloads.
- Correctly running pods: Ensures containers within each pod are running as expected, taking action if something goes wrong.
- Monitoring node and pod health: Tracks the health of the node and its pods, reporting any issues to help maintain stability and performance.
- Managing container lifecycles: Starts and stops containers and manages restarts across the container lifecycle.
Container runtime
The container runtime is responsible for running containers in a Kubernetes environment. It supports multiple runtimes (including Docker, containerd, and CRI-O) and manages essential tasks such as:
- Pulling container images from registries
- Executing containers efficiently
- Isolating resources for stable and secure performance
What are other Kubernetes infrastructure components?
Kubernetes includes several key infrastructure components that work alongside its core functionality. Here’s a breakdown of each component to help you understand their roles:
- Pods: The smallest deployable units in Kubernetes, pods contain one or more containers that share resources and run together as a single unit.
- Deployments: Used to define the desired state for pods and replica sets, deployments allow your application to run smoothly and scale appropriately.
- Services: These create a stable way to manage networking and communication so different parts of your application can interact reliably.
- Namespaces: Provide a way to isolate resources within your cluster, making it easier to organize and manage complex environments.
- Persistent volumes: Keep your data safe by separating storage from individual pods, so it persists even if pods are re-created.
- ConfigMaps and secrets: Help manage configuration and sensitive data efficiently, keeping applications flexible and secure.
Each of these components plays an important role in streamlining application management and enabling smooth scaling within your cluster. By working together, they help simplify complex processes, making it easier to manage and grow your system efficiently.
Interactions between components
Simplified Kubernetes diagram (Source)
The Kubernetes ecosystem relies on well-orchestrated interactions to create a dynamic container management environment. When a deployment request is made, a user submits a configuration through the Kubernetes API. The kube-apiserver validates the request, acting as the entry point for cluster operations. Once validated, the scheduler analyzes the cluster’s state to find the best node for the workload, considering resource availability, hardware constraints, and workload distribution.
Next, the kubelet on the target node pulls the required container images from the registry, while kube-proxy configures network routing to maintain communication within the cluster and with external services. The container runtime then launches the containers, moving the system closer to the desired state.
Kubernetes’ true strength lies in its continuous monitoring and self-healing. Controllers constantly compare the current cluster state with the desired state, making corrections as needed. This includes replacing failed containers, redistributing workloads when nodes fail, and reallocating resources to maintain performance and reliability.
This orchestration of components allows Kubernetes clusters to stay resilient, efficient, and responsive to changing demands. Its ability to monitor, heal, and optimize reduces operational overhead, boosts reliability, and accelerates innovation.
Kubernetes architecture best practices and principles
Building strong use cases for Kubernetes architecture involves following a set of foundational best practices. Let’s break down some of the most important principles to help you design systems that are reliable, scalable, and secure.
Unchanging infrastructure
- Treat containers as disposable. Design your system so containers can be replaced rather than modified in place.
- Avoid making changes directly to running containers. Instead, use declarative configurations to establish consistency and repeatability.
- Rely on versioned, immutable container images to maintain stability and predictability, providing a reliable foundation for your applications.
Microservices design
- Structure your application as loosely coupled services so components can function independently.
- Design each service to scale independently based on demand, enabling better resource allocation.
- Simplify maintenance and updates by keeping services small and focused on specific tasks.
Resource management
- Specify clear resource requests and limits for containers to prevent resource contention and overuse.
- Implement scaling strategies such as horizontal pod autoscaling to adapt to workload changes.
- Monitor resource usage regularly to identify inefficiencies and optimize system performance.
Security considerations
- Protect your cluster with strong authentication mechanisms and limit access to authorized users and systems.
- Use role-based access control (RBAC) to manage permissions, limiting access to what is necessary for each role.
- Keep Kubernetes components and container images up to date with the latest patches to reduce vulnerabilities.
- Minimize container privileges by following the principle of least privilege.
By following these best practices, you can create a Kubernetes architecture that is efficient, scalable, and secure. While challenges may arise, these principles provide a strong foundation to guide your efforts and help you maintain a reliable system.
High availability and scalability
(Source)
Kubernetes is built to deliver high availability and scalability—two must-haves for today’s mission-critical applications. High availability comes from multiple control plane instances to avoid single points of failure, plus leader election strategies that keep core components functional even when individual instances encounter problems.
On the node level, Kubernetes spreads workloads across nodes and uses failover mechanisms to recover from node failures without impacting application performance. For additional resilience, organizations often implement multi-zone or multi-region deployments to add geographic redundancy and protect against larger infrastructure outages.
Scalability is another key feature of Kubernetes. The Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) adjusts the number of pod replicas based on real-time metrics, helping applications handle traffic changes efficiently while optimizing resources. Similarly, the Cluster Autoscaler can add or remove nodes as needed to match workload demands, making scaling more seamless and cost-effective when tuned properly.
Kubernetes can support large-scale operations and thousands of nodes in a single cluster. It uses dynamic resource allocation to distribute workloads intelligently, reducing bottlenecks and improving overall efficiency.
Kubernetes also offers practical ways to keep costs under control by making the most of your resources. Setting pod resource requests and limits helps the scheduler use capacity efficiently, while node sizing and autoscaling can help balance cost and performance. Tools like Prometheus provide usage metrics that inform optimization decisions. For organizations looking to translate usage data into continuous optimization actions, PerfectScale for Kubernetes by DoiT helps rightsize workloads, improve bin-packing, and reduce idle resource waste across clusters. You can also explore the broader platform at PerfectScale.
Optimize your Kubernetes journey with DoiT
Unless you have the right expertise, managing Kubernetes environments can be challenging. At DoiT, we offer Kubernetes optimization and management solutions designed to help your organization tackle these challenges effectively. Our platform focuses on:
- Optimizing cluster performance for smoother operations
- Reducing cloud infrastructure costs to improve budget efficiency
- Streamlining deployment processes to save time and resources
Implement best-practice configurations for long-term success through our GKE Accelerator and EKS Accelerator programs.
DoiT’s platform makes it easier to optimize Kubernetes deployments with real-time scaling insights, cost management features like expense dashboards and rightsizing guidance, and performance improvements like container-level analytics and smarter workload placement. To prioritize automated, always-on Kubernetes cost optimization, start with PerfectScale for Kubernetes by DoiT, and use PerfectScale as a secondary resource for additional product information.
From AWS to Azure, by utilizing DoiT’s Kubernetes accelerators and cloud analytics, you can simplify complex Kubernetes architectures and turn them into a strategic DevOps advantage for your business.
Discover PerfectScale for Kubernetes by DoiT today and see how automated rightsizing and smarter scaling can reduce waste without sacrificing performance. For more product background, visit PerfectScale.